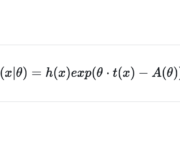Mathematics for Machine Learning Archive
Central Limit Theorem
On February 15, 2021 In Mathematics for Machine Learning, Probability and Statistics
In this post, we build an intuitive understanding of the central limit theorem by looking at some examples. Then, we introducing the formal definition of the CLT. What is the Central Limit Theorem The central limit theorem states that under most conditions, the sum of large numbers of random variables is normally distributed. This
What is the Law of Large Numbers
On February 13, 2021 In Mathematics for Machine Learning, Probability and Statistics
In this post, we introduce the law of large numbers and its implications for the expected value and the variance. The law of large numbers states that the larger your sample size the closer your observed sample mean is to the actual population mean. Intuitively this makes sense. Suppose, you wanted to estimate the
Probability and Statistics for Machine Learning and Data Science
On February 6, 2021 In Mathematics for Machine Learning, None, Probability and Statistics
This series of blog posts introduces probability and mathematical statistics. While I wrote these posts with a focus on machine learning and data science applications, they are kept sufficiently general for other readers. Some familiarity with vectors and matrices, as well as differential and integral calculus, is necessary to fully understand all concepts. If
Factorization Theorem and the Exponential Family
On February 6, 2021 In Mathematics for Machine Learning, Probability and Statistics
In this post we introduce Fisher’s factorization theorem and the concept of sufficient statistics. We learn how to use these concepts to construct a general expression for various common distributions known as the exponential family. In applied statistics and machine learning we rarely have the fortune of dealing with a known distribution with known
Maximum Likelihood Estimation for Gaussian Distributions
On February 1, 2021 In Mathematics for Machine Learning, Probability and Statistics
In this post, we learn how to derive the maximum likelihood estimates for Gaussian random variables. We’ve discussed Maximum Likelihood Estimation as a method for finding the parameters of a distribution in the context of a Bernoulli trial, Most commonly, data follows a Gaussian distribution, which is why I’m dedicating a post to likelihood
Multivariate Gaussian Distribution
On January 30, 2021 In Mathematics for Machine Learning, Probability and Statistics
In this post, we discuss the normal distribution in a multivariate context. The multivariate Gaussian distribution generalizes the one-dimensional Gaussian distribution to higher-dimensional data. In the absence of information about the real distribution of a dataset, it is usually a sensible choice to assume that data is normally distributed. Since data science practitioners deal
Maximum Likelihood Estimation Explained by Example
On January 23, 2021 In Mathematics for Machine Learning, Probability and Statistics
In this post, we learn how to calculate the likelihood and discuss how it differs from probability. We then introduce maximum likelihood estimation and explore why the log-likelihood is often the more sensible choice in practical applications. Maximum likelihood estimation is an important concept in statistics and machine learning. Before diving into the specifics,
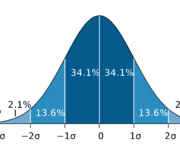
Normal Distribution and Gaussian Random Variables
On January 21, 2021 In Mathematics for Machine Learning, Probability and Statistics
In this post, we introduce the normal distribution and its properties. We also learn how to calculate Z scores and standard deviations from the mean. The normal distribution also known as the Gaussian distribution is the most commonly used probability distribution. The normal distribution curve has the famous bell shape. Many real-world random variables
Bernoulli Random Variables and the Binomial Distribution in Probability
On January 18, 2021 In Mathematics for Machine Learning, Probability and Statistics
In this post, we develop an understanding of Bernoulli random variables and the binomial distribution. We introduce scenarios that follow the binomial distribution and learn how it relates to the normal distribution. The Bernoulli Distribution A Bernoulli random variable can be used to model the probability of a system whose outcome can only result
Covariance and Correlation
On January 15, 2021 In Mathematics for Machine Learning, Probability and Statistics
Int this post, we introduce covariance and correlation, discuss how they can be used to measure the relationship between random variables, and learn how to calculate them. Covariance and Correlation are both measures that describe the relationship between two or more random variables. What is Covariance The formal definition of covariance describes it as