Software Design Archive
What is the Liskov Substitution Principle: An Explanation with Examples in Java
On September 18, 2022 In Design Patterns, Software Design
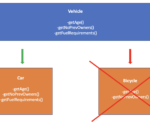
In this post, we will understand the Liskov substitution principle and illustrate how it works with an extended example in Java. The Liskov substitution principle states that an object of a superclass should be replaceable with an object of any of its subclasses. It is one of the SOLID design principles in object-oriented software
What is the Open/Closed Principle: An Explanation with Examples in Java
On August 17, 2022 In Design Patterns, Software Design
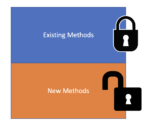
The open-closed principle states that classes and modules in a software system should be open for extension but closed for modification. It is one of the SOLID principles for software design.In this post, we will build a step-by-step understanding of the open/closed principle using examples in Java. Why Should You Apply the Open/Closed Principle?
The Single Responsibility Principle
On June 19, 2022 In Design Patterns, Software Design
What is the Single Responsibility Principle? The SRP is often misinterpreted to stipulate that a module should only do one thing. While designing functions only to have one purpose is good software engineering practice, it is not what the single responsibility principle states. In a nutshell, the single responsibility principle is one of the
Hashing in Java
On July 13, 2021 In Data Structures, Software Design
In this post, we will discuss hashing in Java and introduce a few data structures such as hashtables and hashmaps that rely on hashing. What is Hashing? Hashing is a technique that allows a program to store and subsequently find an object in a large collection of items without going through every item. A
Priority Queue in Java: A Complete Introduction
On July 8, 2021 In Data Structures, Software Design
In this post, we introduce the priority queue in Java and explain the underlying concept of a heap. What is a Priority Queue in Java? In a priority queue, items are ordered alphabetically in ascending order, numerically in ascending order, or according to a user-defined attribute based on a custom comparator. In a priority
The Queue in Java
On June 22, 2021 In Data Structures, Software Design
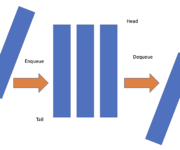
In this post we learn how to implement a queue in Java using the linked list and priority queue data structures provided by Java. What is a Queue in Java? A queue is a data structure in Java and many other programming languages. Elements are added according to the FIFO (first-in, first-out) principle. An
The Stack in Java
On June 21, 2021 In Data Structures, Software Design
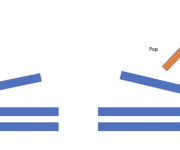
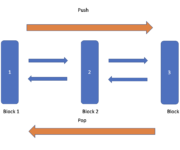
In this post we look at the stack in Java, a data structure that operates on the LIFO principle. We discuss (clicking the link will take you to the section): What is a Stack How to implement a Stack using collections and deque How to implement a Java stack from scratch What is a
How to Learn Java: A Comprehensive Guide
On June 18, 2021 In Software Design
Java is one of the most widely used programming languages in the world today. It powers applications ranging from enterprise software systems to Android apps. Learning it can open the door to plenty of well-paid job opportunities. People who have mastered the art of developing software in Java are hot commodities in the job
An Introduction to Java Arrays
On June 16, 2021 In Data Structures, Software Design
In. this post we introduce and define the array data structure in java, how to use it and what common operations can be performed using arrays. What is an Array in Java? An array is a fixed-length Java container object that contains other objects of the same type. An array’s length and the type
Python Collections Module
On June 10, 2021 In Data Structures, Software Design
In this post, we will introduce the collection module in Python, which provides a range of container types for object storage. We introduce the concept of a container in Python and then we go through the available container types. What is a Container in Python? Containers in Python are meta-objects that can hold an